Return to: Neck Surgery Protocols
Overview
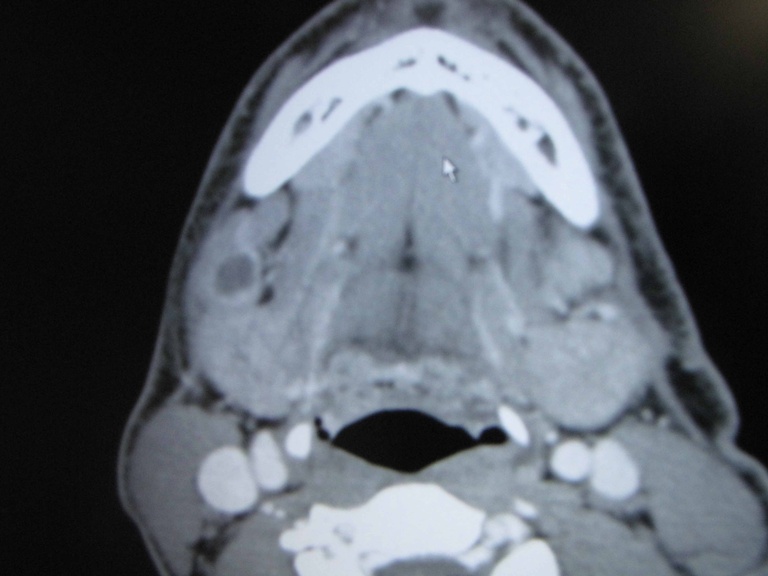
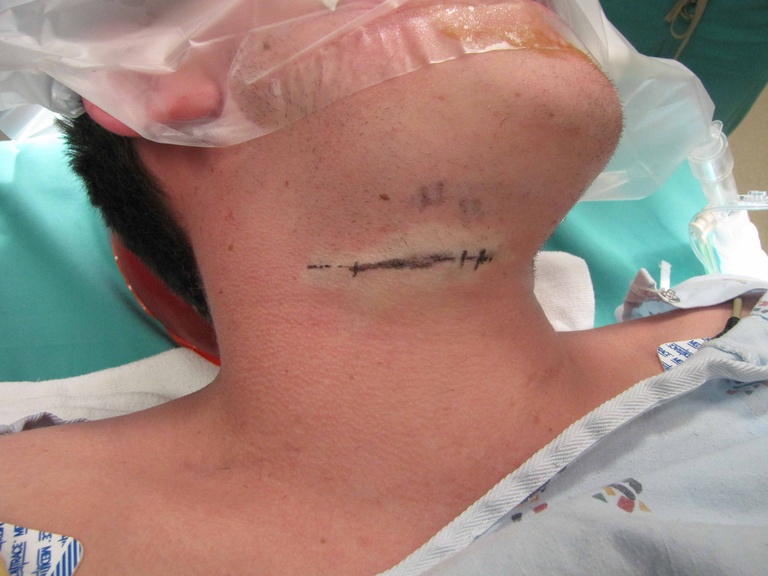
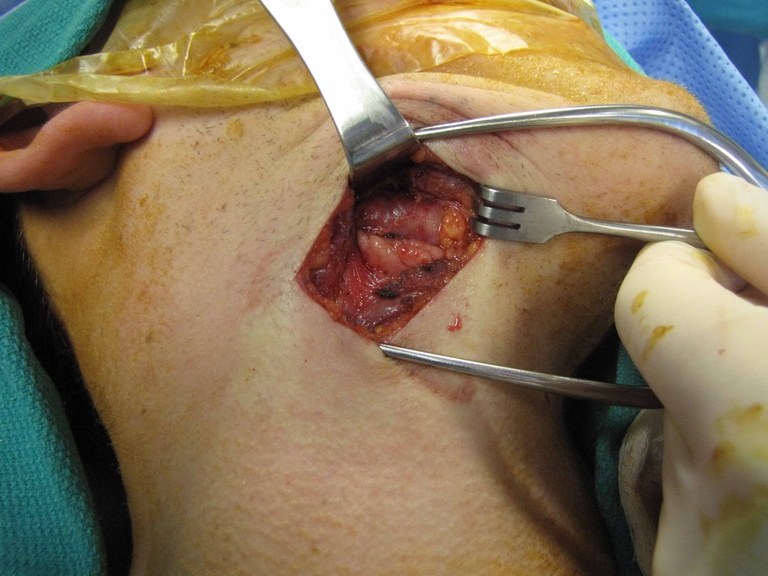
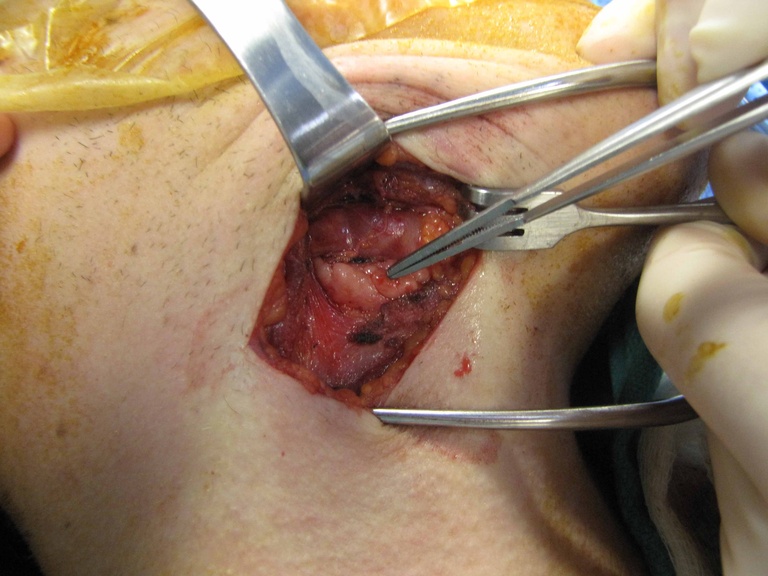
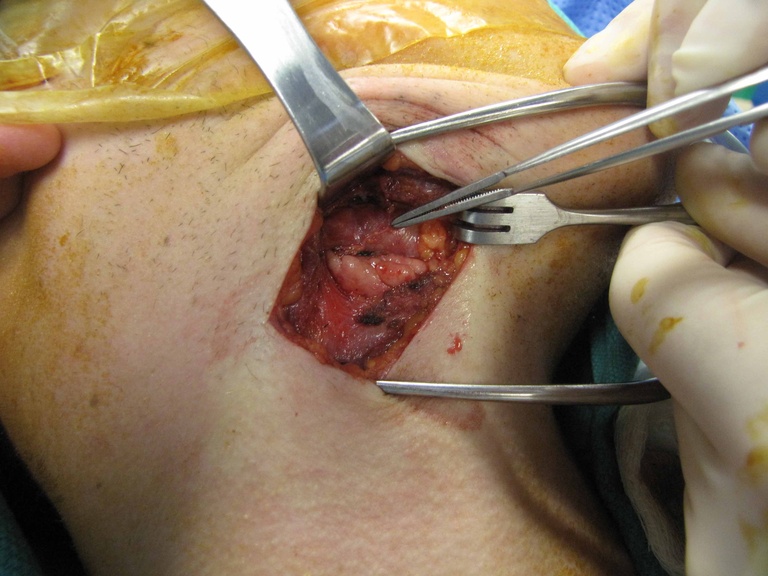
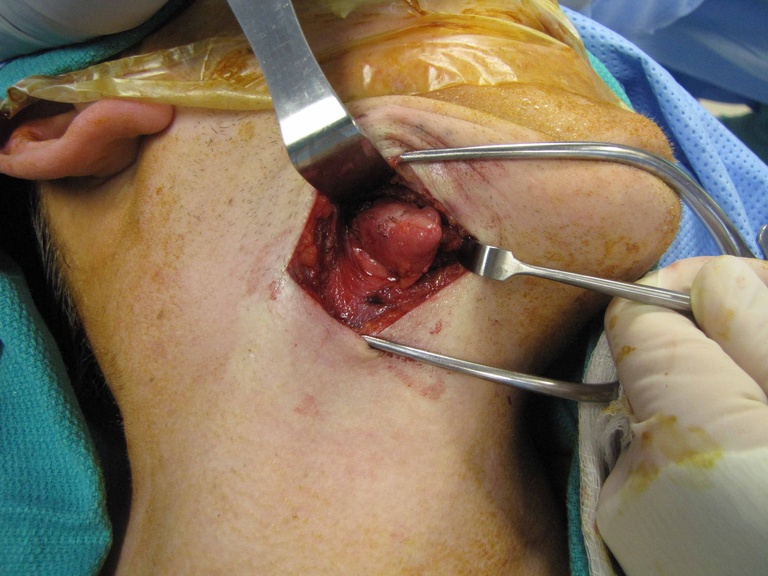
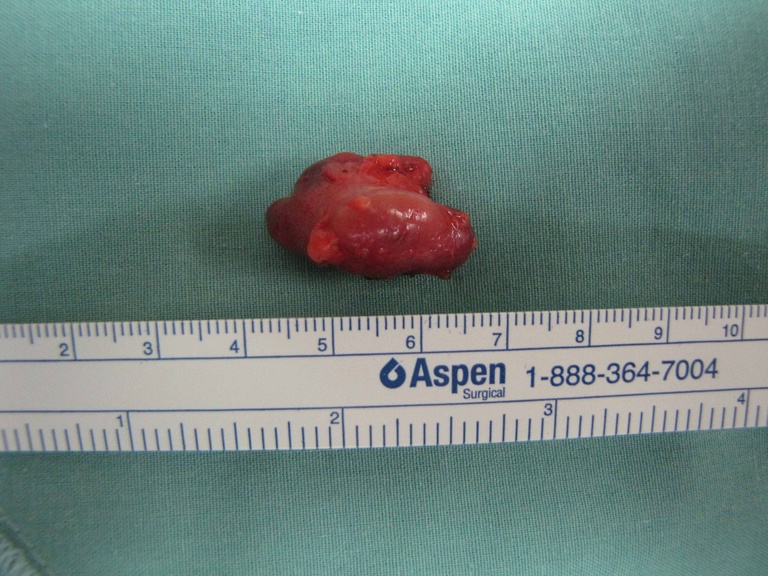
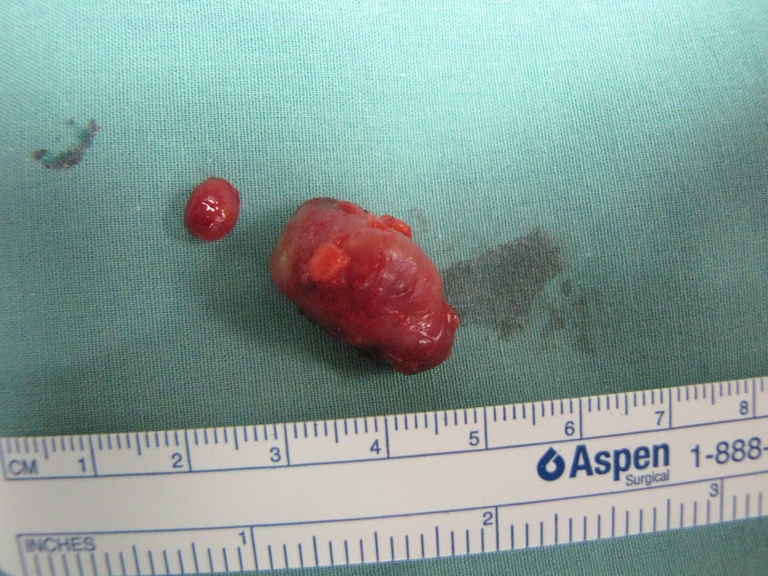
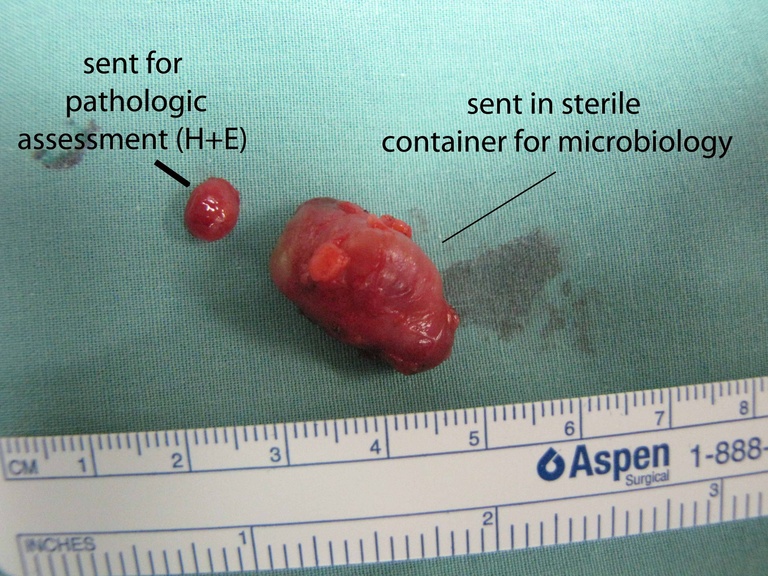
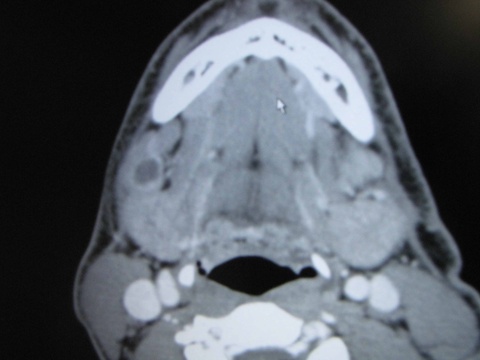
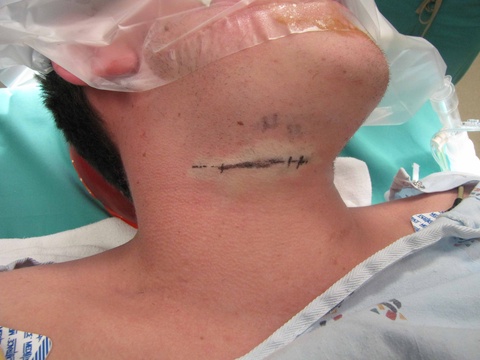
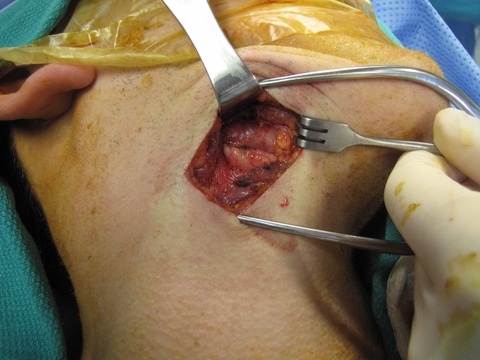
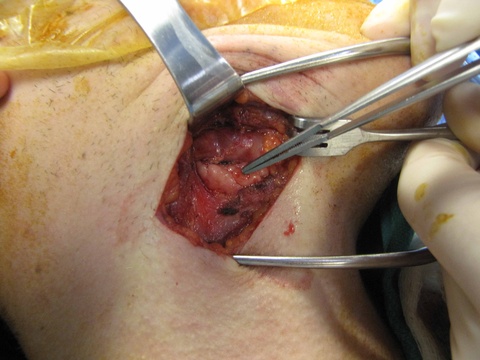
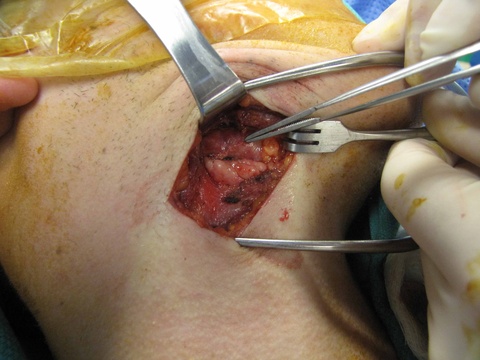
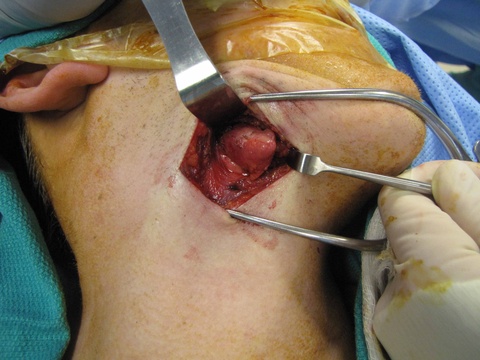
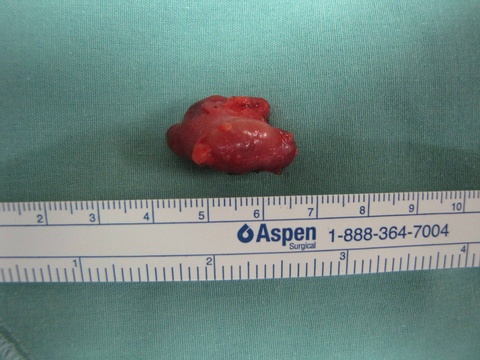
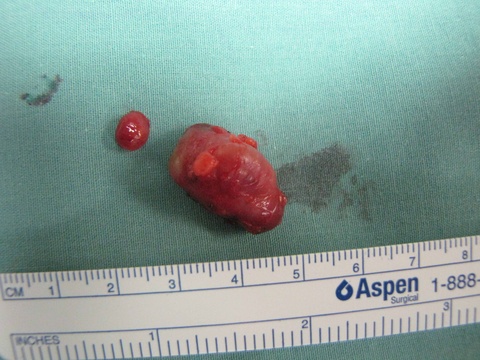
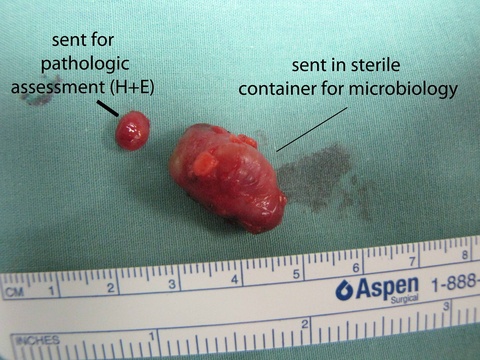
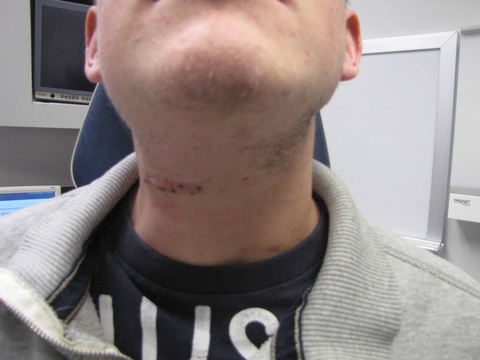
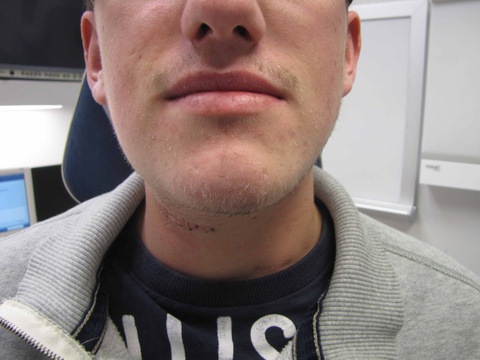
Chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) represents a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by defective function of human phagocytes (neutrophils, mononuclear cells, macrophages, and eosinophils). The disease manifests as repeated, severe bacterial and fungal infections (Song et al 2012). In the case pictured below, excision of an infected lymph node (rather than needle biopsy) was requested by the infectious disease service both to institute treatment (removal of infected tissue) and permit full microbial assessment for pathogens.
Level IB Enlarged Lymph Node CGD | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
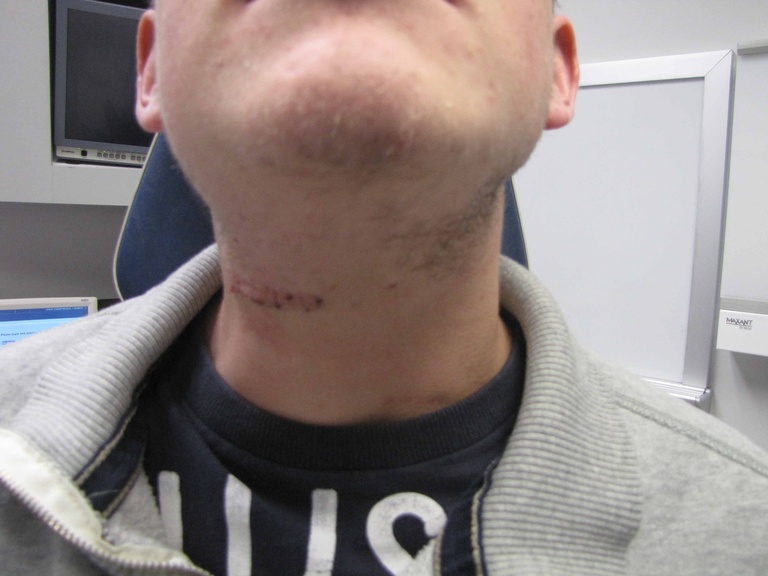
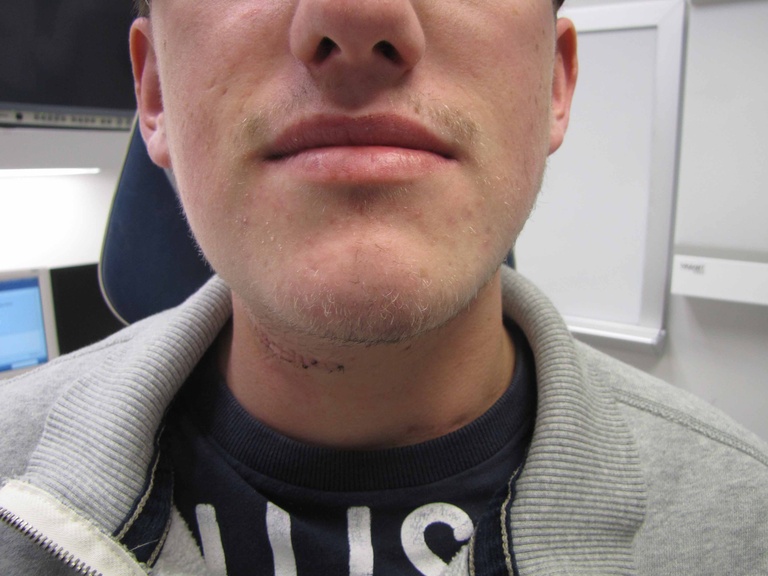
| Postop day 6 suture removal | Postop day #6 suture removal | ||
References
Song et al: Chronic granulomatous disease: a review of the infectious and inflammatory complications. in Clinical and Molecular Allergy 2011, 9:10 http://www.clinicalmolecularallergy.com/content/9/1/10