General
- Also known as carotid body tumor, chemodectoma, and non-chromaffin paraganglioma
- A benign vascular tumor originating from glomus bodies in the carotid body at the common carotid bifurcation (Hoang et al. 2019)
Paragangliomas
- Paragangliomas are tumors of neuroendocrine cells associated with the sympathetic or parasympathetic nervous system
- Types of paragangliomas include: carotid body tumors, glomus jugulare tumors, glomus tympanicum tumors, and glomus vagale tumors all within the head and neck, as well as pheochromocytomas
- The majority are solitary, but if multiple paragangliomas are present, consider MEN 2a or MEN 2b (Ikram and Rehman 2022)
- Paragangliomas are benign but locally invasive and highly vascularized
Radiologic Findings
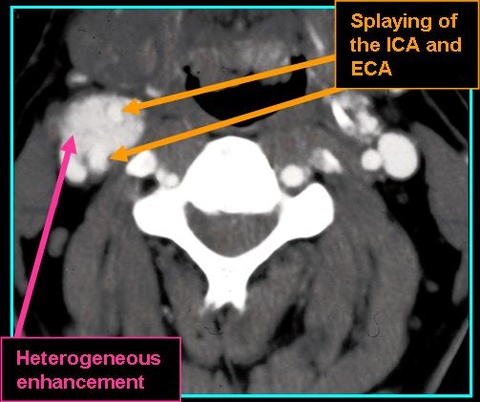
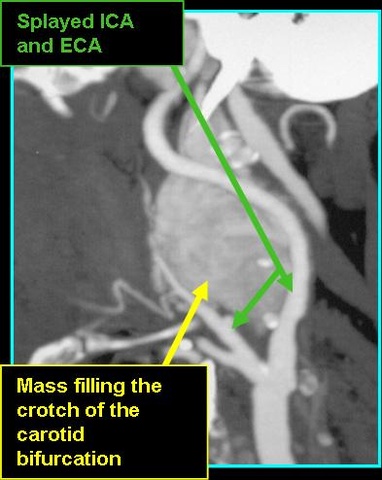
- Look for splaying of the ECA anteromedially and the ICA posterolaterally
- Found in the carotid space just above the hyoid bone in the crotch of the carotid bifurcation
- Size at presentation is typically 1-6 cm with an ovoid, lobular appearance
- On CT: splaying of ECA and ICA and density like that of muscle without contrast, avidly enhancing mass extending
- with contrast
- On MR: "pepper" (black dots) and "salt" appearance (white dots - uncommon) on T1, hyperintense and good spread definition on post-contrast T1
- Most commonly seen in patients in their 40s and 50s
References
Hoang VT, Trinh CT, Lai TAK, Doan DT, Tran TTT. Carotid body tumor: a case report and literature review. J Radiol Case Rep. 2019;13(8):19-30. Published 2019 Aug 31. doi:10.3941/jrcr.v13i8.3681
Ikram A, Rehman A. Paraganglioma. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; September 5, 2022.