See also:
Carotid Body
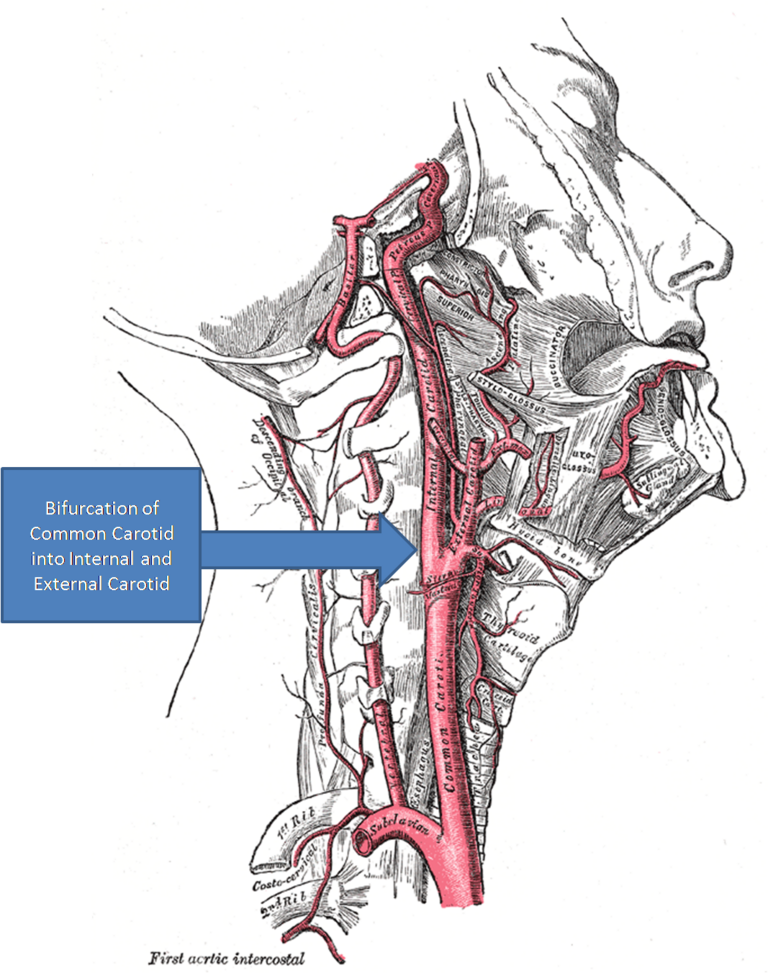
- The carotid body is a chemoreceptor located in the adventitia of the bifurcation of the common carotid artery
- Chemoreceptor function (Iturriaga et al. 2021)
- Carotid body monitors the blood’s pH, pCO2, and pO2 and thereby modulates cardiovascular and respiratory function primarily through sympathetic tone
- When the carotid body senses acidemia, hypercapnea, or hypoxia, autonomic firing leads to increased blood pressure, heart rate, and respiratory rate
- The function of the carotid body is complemented by other chemoreceptors, most notably the aortic body located in the aortic arch
- Anatomy (Day et al. 2021)
- Located in the bifurcation of the common carotid artery
- Average size of carotid body is 3-5 mm in diameter and average weight is 12 mg
- Blood supply: from external carotid through Mayer’s ligament (provides attachment to carotids)
- Innervation: Hering’s nerve (aka carotid sinus nerve), a branch of the glossopharyngeal (CN IX), originating 1.5 cm distal to jugular foramen
- Composed of two receptor cell types (Iturriaga et al. 2021):
- Chief cells (Type I): derived from neural crest, release ACh, ATP, dopamine in response to activation
- Sustentacular cells (Type II): supporting cells
Carotid Sinus
- The carotid sinus is a baroreceptor that senses changes in systemic blood pressure and is located in the adventitia of the carotid bulb of the internal carotid artery
- Due to its location, the carotid sinus is an intimately related but distinct organ from the carotid body
- Innervation: same as carotid body (Hering’s nerve, aka carotid sinus nerve, a branch of CN IX)
- The function of the carotid sinus can be affected by carotid body tumor resection
- Carotid sinus syndrome (syncopal episodes due to inadvertant triggering of the carotid sinus) is a pathology of the carotid sinus; in addition, carotid massage triggers the carotid sinus pathway (increased pressure on carotid sinus due to massage → sends signal to decrease systemic BP) (Amin and Pavri 2015).
References
Iturriaga R, Alcayaga J, Chapleau MW, Somers VK. Carotid body chemoreceptors: physiology, pathology, and implications for health and disease. Physiol Rev. 2021 Jul 1;101(3):1177-1235. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00039.2019. Epub 2021 Feb 11. PMID: 33570461; PMCID: PMC8526340.
Day, Terry A. and Albergotti, W Greer: Neoplasms of the Neck Ch 115, 1755-1772.e3 in Cummings Otolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery 7th Edition 2021 Elsevier, Inc.
Amin V, Pavri BB. Carotid sinus syndrome. Cardiol Rev. 2015 May-Jun;23(3):130-4. doi: 10.1097/CRD.0000000000000041. PMID: 25211534.
Netterville, James L., et al. "Carotid body tumors: a review of 30 patients with 46 tumors." The Laryngoscope 105.2 (1995): 115-126
Gray513.png: Henry Grayderivative work: Skoch3, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons